Closed Loop System
A closed-loop control system is to control the system in which the control is dependent on the output. For example, control of water level in a tank, refrigerator system, etc.
But do you think, this is enough? No right!
Certain questions must puzzle our minds. Questions like, what is a System?
What is a Control System & its components?

Let us try finding out the answers to all of these. Also, I would suggest going through the open-loop system for a better understanding of this topic.
What is a System?
A system is a combination or an arrangement of different physical components which act together as an entire unit to achieve a certain objective.
Every physical object is a system. A classroom is a good example of a physical system. A room along with the combination of benches, blackboard, fans, lighting arrangements, etc. can be called a classroom that acts as an elementary system.
Another example of a system is a lamp. A lamp made up of glass, the filament is a physical system. Similarly, a kite made up of paper and sticks is an example of a physical system.
Therefore, a system can be of any type i.e., physical, ecological, biological, etc.
Control System
As the name suggests, to control means to regulate, to direct or to command. Hence a control system is an arrangement of different physical elements connected in such a manner to regulate, direct or command itself or some other system.
Let us understand this control system more practically.
Imagine you are sitting in your classroom and your teacher is delivering his lecture. This combination becomes a control system as, he tries to regulate, direct or command the students to achieve the objective. The objective is of course to input good knowledge to the students.
Similarly, if a lamp is switched ON or OFF using a switch, the entire system can be called a control system.
I guess now you are comfortable with these terminologies.
Aren’t you?
Therefore, in short, a control system in the broadest sense, an interconnection of the physical components to provide the desired function, involving some kind of controlling action in it.
Components of Control System
Let us learn the physical components of any control system.
Plant
The portion of a system that is to be controlled or regulated is called the plant or the process.
Controller
The controller is an element of the system itself or external to the system which controls the plant or the process. For each system, there must be an excitation and the system accepts it as an input. And for analyzing the behavior of the system for such input, it is necessary to define the output of the system.
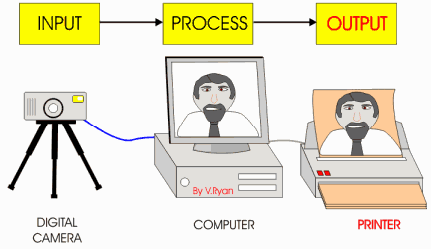
Input
It is an applied signal or an excitation signal applied to a control system from an external energy source to produce a specified output.
Output
It is the particular signal of interest or the actual response obtained from a control system when input is applied to it.
Disturbances
The disturbance is a signal which tends to adversely affect the value of the output of the system. If such a disturbance is generated within the system itself, it is called an internal disturbance. The disturbance generated outside the system acting as an extra input to the system in addition to its normal input, affecting the output adversely is called an external disturbance.
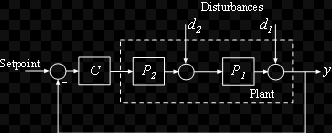
Control systems may have more than one output. From the information regarding the system, it is possible to well define all the inputs and outputs of the systems.
Hence, the input variable is generally referred as the reference input and output is generally referred as the controlled output.
Well, I hope you are much more confident after gaining all this knowledge.
Cool!! Let’s move forward and learn some basic concepts of the control system. This will help us understand the closed-loop system in a better way later.
Basics Concepts of Control Systems
In a control system, there is an interconnection between the constituent components. These individual components may be electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, thermal or chemical. A well-designed control system will provide the best response for the complete system to external, time-dependent disturbances operating on the system. The basic functions of the control systems are:
- To minimize the error between the actual and the desired output.
- Minimizing the time response to load changes in the system.
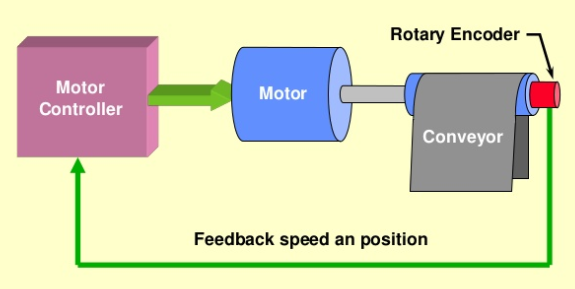
A simple example of a control system is a water level controlled system in a tank. in this, the pump is switched ON for an interval that would allow enough discharge of liquid into the tank to fill it. Once the tank is filled to the required level, the pump will switch OFF.
The system has an input from the water level sensor that notifies it what the liquid level is. Then compare this data with what the level should have been and provides the appropriate response to obtain the required water level in the tank. This is an example of feedback control in which the sensor signals are given feedback from the output to modify the reaction of the pump to switch ON or OFF. Feedback control is exercised by the control system, which compares the actual output of the system with the desired, and adjusts the output accordingly.
Therefore, the concepts of the control system are clear. But there arrives one more question.
Aren’t you willing to know why do we need a control system?
Of course, yes. Then let’s go ahead with more enthusiasm.
Requirement of a (Closed) Control System
Well, you must be wondering why I have mentioned closed in the above heading! Don’t worry, you will get your answer in another few minutes.
The three important requirements of a control system are as follows:
Stability
For any change in the input signal, the output of the system reads or makes its response at a reasonable value.
Accuracy
The closeness of the measured value to the true value is known as accuracy. In practice, the measured value differs from the true value.
Response
The quickness with which an instrument responds to a change in the output signal is known as the response.
An ideal system has perfect stability, 100% accuracy, and immediate or instantaneous response. Practically, this is not possible but a slight compromise can be made in these above-mentioned requirements.
Well, all these requirements are best fulfilled by a closed-loop control system. This is because it has a feedback path.
Let us know have a look at the classification of the control system.
Classification of Control System
A control system can be classified as :
- Open Loop Control System
- Closed-Loop Control System
To have a better understanding of the closed-loop system, knowledge of the open-loop system is very important. So if you are not clear with the concepts, then please go to the Open-loop system and come back.
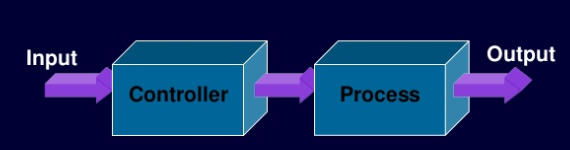
Well, there might be a question coming to your mind.
What is the need of the closed-loop system? The answer is in the disadvantages of the open-loop system.
Yes, it is. Let us understand more clearly.
Disadvantages of Open Loop System
I am hoping that you are good with the open-loop system and directly jumping to its disadvantages. These are:
- It is not suitable for precise works.
- The error cannot be corrected.
- The control action depends upon the input command.
- The presence of non-linearity can result in malfunctioning.
Now, many of the systems need precision. This is possible only with feedback. Also, an error elimination process needs feedback. One more important factor is the disturbance which acts as input at times.
Therefore, without feedback and error elimination, getting the desired output is difficult.
Closed Loop System
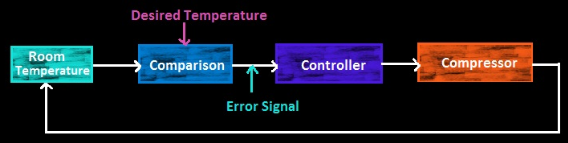
The closed-loop control system is nothing but an extension of an open-loop control system. One measurement unit (sensor) calculates the difference between the desired and the measured values and gives it back to the input as feedback.
Example of a Closed Loop System
As you can see in the figure, imagine an electric heater. The temperature should be controlled by the system to maintain uniform heating throughout the ironing process. However, in an open-loop system, switching OFF and switching ON of the iron box are done manually after reaching the required temperature. Therefore, we are not able to predict the required temperature exactly at each & every instant during switching ON and switching OFF.
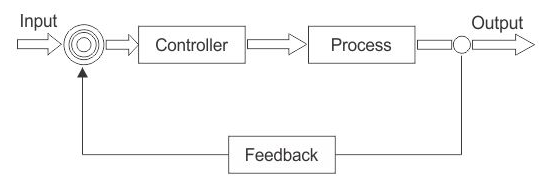
If the temperature exceeds the desired value, it will damage the cloth during ironing. These difficulties are overcome by using a closed-loop system. Here, a temperature sensor is used in the box to sense the temperature. The feedback unit in the closed-loop system senses the temperature at each and every instant when the temperature falls below or goes above the threshold value. Owing to this, the feedback unit will automatically turn ON the supply.
Therefore, the feedback unit sends the output signal to the error detector unit to give an error signal after comparing it with the reference value(desired). This error signal takes necessary control action when it is applied to the controller(see in figure). In fig, the controller is the switch, heater & plant is the process.
Advantages of Closed Loop System
- The feedback signal controls the output accurately.
- Change in the system is automatically taken care of.
- Control action depends upon feedback.
- Increased accuracy.
- Reduced sensitivity of output to input ratio.
- Better linear characteristics.
- Improved bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Closed Loop System
- The system is complicated and expensive.
- The system may become unstable.
