Touch Sensor working principle
The Touch Sensor is sensitive to touch, pressure as well as force. The Touch Sensor works similar to that of a simple switch.
When there is contact or a touch on the surface of the Touch Sensor. It acts like a closed switch and allows the current to flow through it. When the contact is released it acts similar to the opened switch and hence there is no flow of current.
In the below picture you can understand how the touch sensor works.
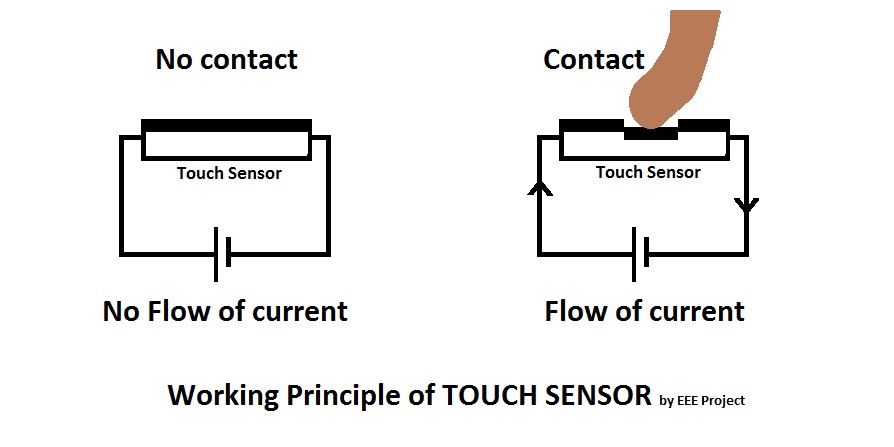
Working of different Touch Sensors
Below is the working of the two type of sensors are explained in detail.
Capacitive touch sensor
The Capacitive touch sensors are very popular since they are more robust, durable, and user friendly. Moreover, it is also cost-effective when compared to resistive touch sensors.
The capacitive sensor is made just similar to the normal capacitor. There are two conductors separated from the insulator.
In case of the sensor, the metal plates are used as the conductors. The capacitance of the sensor can be expressed as below.
C = ε0 x εr x A / d
Where,
ε0 represents the permittivity of free space
εr represents the relative permittivity or dielectric constant
d represents the distance the parallel plates and A represents the area of the plates.
We know that if the plate has more area the more capacitance it will produce and the more distance between the two plates are the less capacitance will become.
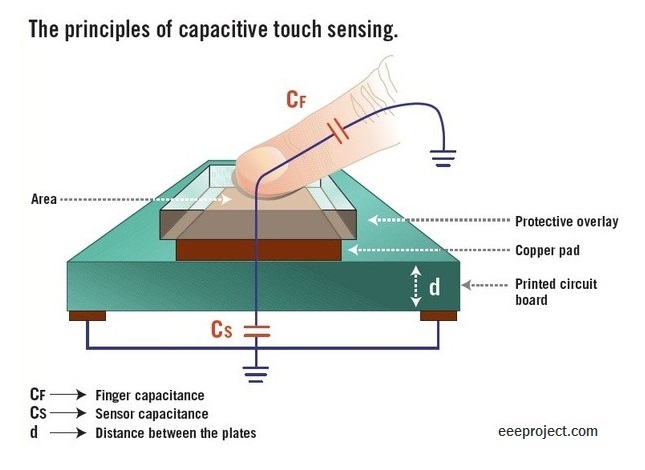
In the Capacitive touch sensor, there are two parallel plates that form a capacitor with the capacitance value represented as C0. As we touch the sensor through our finger, our finger acts as a conductive object and hence produces a capacitance value of CT as shown in the figure below.
In the application of a sensor, the capacitance C0 is measured continuously with the help of the capacitance measurement circuit. There will be an uncertain increase in the capacitance if any conductive object such as our finger touches the plate. The capacitance measuring circuit will detect the change in the capacitance and will convert it into a signal.
Working of Capacitive touch sensor
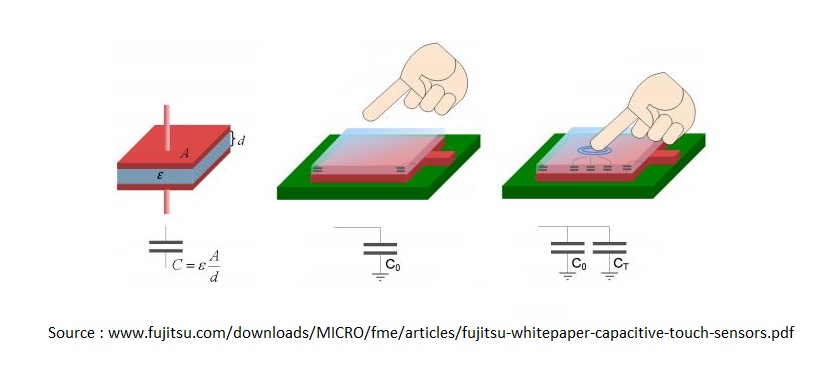
If the parallel plates have a more larger area and the thickness of the insulator is very less then there would be the greater value of the touch capacitance (i.e. CT). Therefore the difference of the capacitance value when the plate is touched and the plate is untouched will be greater.
So, by controlling the size of the parallel plate and the thickness of the insulator we can control the sensitivity of the Capacitive touch sensor.
The Capacitive touch sensor, however, has few drawbacks such as there could be a false trigger since all it needs is to be in a contact with a conducting material and does not require a pressure to operate.
Resistive touch sensor
Unlike the capacitive touch, the resistive touch sensor does not depend on the electrical properties such as the conductivity of the metallic plates.
The resistive sensor works by sensing the pressure when applied on the surface.
Since there is no need to measure the difference in the capacitance the resistive touch sensor can operate on non-conductive materials such as pen, stick, or finger inside the gloves.
The resistive touch sensor consists of the two conductive layers which are separated by a very small distance or dots. The two layers (i.e the top as well as the bottom layer) are made up of a film. The films are generally coated by the Indium Tin Oxide which is a good conductor of electricity and is also transparent in nature as well.
A constant voltage is applied across the surface of two films. When the pressure is applied with the help of the finger or a stick on the top film, the sensor is activated and senses the touch.
The sensor operates when enough pressure is applied, the top film touches the bottom film. When the two film touches each other they create the potential drop. The point of contact of the two films creates the voltage divider at that particular coordinate on the X-Y plane assumed at the film.
The change in the voltage hereby detected by a controller circuit and the location (coordinate) at which the voltage divider created is calculated.
The coordinate of the voltage divider interns of the X and Y axis created as the position of touch at which pressure is applied.
Working of Resistive Touch Sensor
Below circuit illustrates that how the resistive touch sensor works.
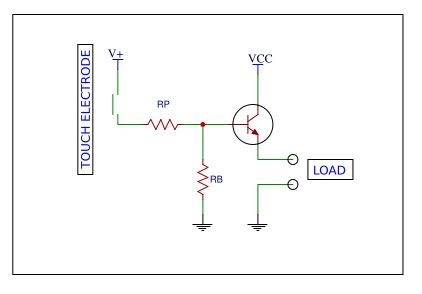
The above circuit shows the basic working of the touch sensor which consists of the touch electrode or the surface.
The resistive touch sensor operates when an object with some resistivity such as our finger touches the surface. Touch of the object with a little resistance forms a close circuit which allows a small amount of current to flow.
In the above circuit the touch causes a very little current to flow.
- The transistor amplifies the voltage to some significant value.
- Resistance Rp is used to protect the transistor from the high current. It is useful In case if there is a fault occurs in the electrodes.
- Resistance Rb is used to keep the base of the transistor grounded. There is no current when there is an open circuit or if there is no pressure applied.
When the little pressure is applied to the electrode. There is a small flow of current through the base of the transistor. The current enables the resistive touch sensor and the current flows through the load.
“You may like to watch FM transmitter circuit working and application“
Resistive Touch Sensor Circuit
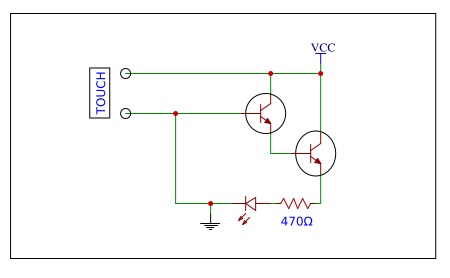
The above circuit consists of the two electrodes, two transistors that are connected as Darlington pair, an LED and a resistor.
When the electrodes are touched or the pressure is applied on the top of the surface. The circuit gets complete and the current gets amplified through the transistors.
The LED indicates the pressure applied or the touch. The resistance is used to prevent the LED from the amplified voltage.
Working principle of a touch sensor
In the present scenario, touch sensors are also known as tactile sensors. The basic working principle of a touch sensor is that it detects near proximity (also known as touch) without depending on physical contact. In simple words, you can understand that its working is the same as a simple switch or circuit.
When any physical medium comes in contact with the touch surface. The internal circuit will be closed inside the sensor and current starts flowing. On the other hand, when this physical contact is broken or released, the circuit will be opened.
Hence, there will be no flow of current. The touch sensors are classified into two categories
- Capacitive touch sensor
- Resistive touch sensor.
You may also like to see Motion detector circuit working and application
Types of Touch Sensor and its application
You can very easily spot the Touch Sensors in various applications in your daily life.
As per their functions, the Touch Sensors are classified into two types which are used in different circumstances and utilities.
Capacitive Touch Sensor
Since these sensors can be produced very easily at a very large scale can be made at very less cost and are very attractive in design. These are widely used in iPods, mobile phones, home appliances, automotive, and many other industrial applications. They are used in applications such as measuring pressure, acceleration, distance, etc.
Resistive Touch Sensor
Unlike the above, these sensors can not sense the small contact or touch. Resistive Touch Sensor requires an amount force to operate, so they are used in applications such as Foot pronation monitoring, musical instrument, keypads (mostly used in old mobile phones), resistive touch-pads, and many other applications.
FAQs about Touch Sensor
1. How does the touch sensor work?
The sensor act as a closed switch when there is a contact to the surface. That allows the flow of current through it.
Touch Sensor working principle
2. What are the applications of Touch Sensor?
3. What is a touch sensor used for?
- Capacitive Touch Sensors are used in smartphones, home appliances, automotive, and other industrial applications.
- Resistive Touch sensors are used in Foot pronation monitoring, musical instrument, keypads, and old mobile phones.
Do share your thoughts about the article in the below comments. You may ask any query or suggest something better than discussed in the article.

7 thoughts on “Touch Sensor Working Principle and Application”
very informative, thanks
IS this what we use in our smartphones ?
Nicely understood ! thanks !
Hi I want to interface the touch-sensor modules using Arduino UNO for Home automation to controlling relay but the garbage value are present in it i think it was switch bouncing and i used capacitor 0.1uf to deboubce the switch but was not stabled how to avoid this garbage values give some suggestions
I connected 1NF and it is working fine with esp32
Hi i try to interface TT223 (touch Sensor )module to node mcu for home automation based project it was working but the sensitivity of the touch was very fast how to increase avoid this can i try with debouncing method ????
Can you call me please, or let me know how/when I can call you, to discuss the application of two or more touch sensors in a new medical application.
Mike Rink
907-903-7432
Punta Gorda, Florida USA